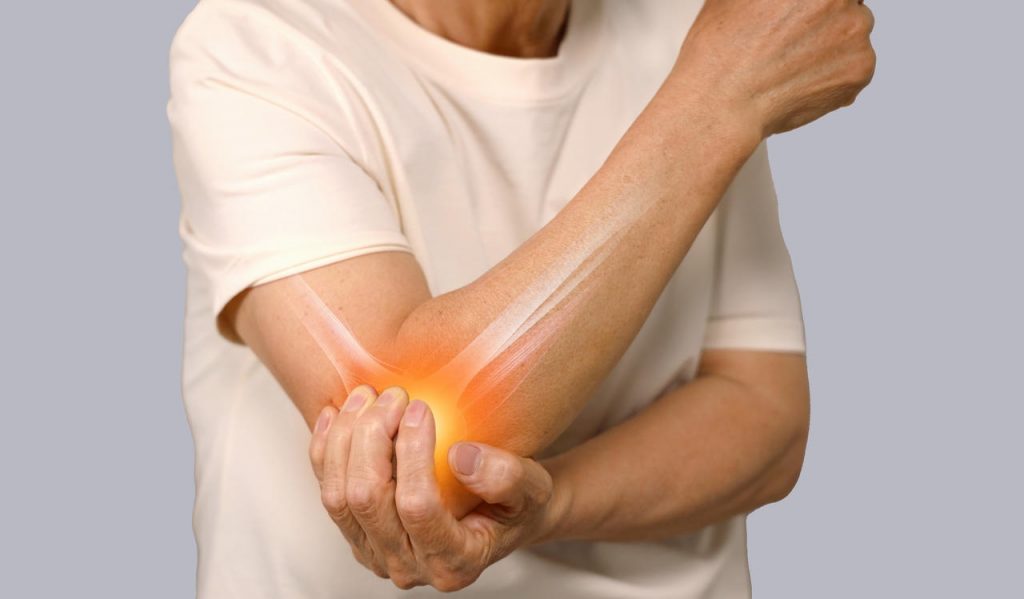
Being physically active and engaging in sports provides numerous health benefits. However, sports and repetitive physical activities also come with the risk of injury, especially for athletes who continuously push their limits. One common condition that affects both professional and recreational athletes is tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis).
Understanding what causes tennis elbow, its symptoms, and the best treatment options is crucial for both prevention and recovery.
What Is Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)?
Tennis elbow, medically known as lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition caused by overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons. It occurs when repetitive movements like gripping, twisting, or lifting strain the tendons that attach to the outer part of the elbow (lateral epicondyle). This leads to tiny tears, inflammation, and irritation, making simple tasks like shaking hands, turning a doorknob, or even lifting a cup uncomfortable.
Interestingly, although many tennis players have a higher risk of experiencing this condition, it is not limited only to those athletes. Anyone who performs repetitive arm motions, such as painters, carpenters, office workers, or musicians, may develop this condition.
What Are the Symptoms of Tennis Elbow?
Tennis elbow develops gradually, often starting with mild discomfort that intensifies over weeks or months. The discomfort is not confined to just the elbow as it can radiate down the forearm and into the wrist.
Common symptoms of tennis elbow include:
- Persistent sharp pain on the outer elbow
- Weakened grip strength
- Stiffness and tenderness
- Swelling or mild inflammation around the elbow joint
What Causes Tennis Elbow?
Tendons around the elbow, particularly the extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) tendon, are responsible for wrist extension and forearm movement. When subjected to excessive stress, they develop tiny tears (microtraumas) leading to inflammation, pain, and reduced grip strength.
These tiny tendon tears are typically caused by:
- Sports-related Strains: Playing tennis, squash, racquetball, fencing, or weightlifting
- Work and Daily Activities: Doing carpentry, painting, typing, using tools, or playing musical instruments
- Sudden Elbow Injury: A direct elbow impact or forceful strain may trigger tennis elbow
In some cases, tennis elbow develops without a clear cause. Therefore, consult an orthopaedic doctor if you experience symptoms.
What Are the Risk Factors for Tennis Elbow?
While anyone can develop this condition, certain factors increase the risk. Despite its common association with sports, it is not exclusive to athletes.
Other risk factors may include:
- Age: People between the ages of 30 and 60 have a higher risk due to ageing.
- Obesity: Extra body weight puts more strain on tendons, increasing the risk.
- Certain Medications: Using certain medications, such as fluoroquinolone antibiotics, can increase the risk, as these can weaken tendons.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to tendons, which can impair healing.
What Are the Potential Complications of Tennis Elbow?
Most cases of tennis elbow improve with rest and proper treatment; however, complications may arise when the condition is left unmanaged or subjected to excessive strain.
Potential complications of tennis elbow include:
- Chronic Pain and Recurrent Injury: If the elbow is overused before healing, microtears in the tendon can worsen, leading to persistent pain that lasts months or even years.
- Tendon Rupture: Repeated strain or steroid injections into the tendon can weaken it over time, increasing the risk of complete rupture, which often requires surgery.
- Surgical Risks (if required): While surgery for this condition is typically a last resort, potential risks include nerve injury, infection, excessive scar tissue formation, and lateral ulnar collateral ligament damage, which can lead to elbow instability.
How Is Tennis Elbow Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of this condition primarily relies on clinical evaluation. A thorough history, physical examination, and specific movement tests help pinpoint if the pain originates from the elbow tendons.
- Medical History and Symptoms: A healthcare specialist will ask about your symptoms, when they started, and any activities that worsen or relieve them. Information about occupation, sports involvement, and repetitive arm movements is considered.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will check for tenderness at the lateral epicondyle (outer elbow). You may be asked to move your wrist, elbow, and fingers to assess pain levels. Resistance tests may be used, such as extending the wrist while applying pressure to detect discomfort.
- Imaging Tests: In some instances, imaging tests are used to exclude other potential causes. These tests may include:
- X-ray: Rules out other causes of inflammation, such as arthritis or fractures in the elbow
- Ultrasound: Provides real-time images of tendon damage and inflammation
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Identifies the severity of tendon injury and checks for nerve compression or spinal issues that might contribute to arm pain
- Electromyography (EMG): Assesses nerve function to rule out nerve-related conditions mimicking tennis elbow
How to Prevent Tennis Elbow
Preventing tennis elbow involves adopting proper techniques, modifying activities, and strengthening forearm muscles. Here are some key tips for work and sports:
- Minimise repetitive strain on elbow tendons
- Strengthen forearm muscles
- Maintain good flexibility
- Distribute load to larger muscle groups
- Optimise your workstation ergonomics
- Keep wrists in a neutral position
- Always perform proper warm-up and cool-down routines
- Use correct technique and form
- Prioritise recovery and post-activity care
FAQs About Tennis Elbow
Can tennis elbow affect both arms?
While it most commonly affects the dominant arm, tennis elbow can occur in both arms—especially in individuals with bilateral repetitive stress from sports or work.
Can tennis elbow affect both arms?
While less common, tennis elbow can affect both arms, particularly with equal repetitive stress. However, it typically develops in the dominant arm.
What’s the difference between a tennis elbow and a golfer’s elbow?
While both conditions are caused by overuse of the forearm muscles, a golfer’s elbow affects the inside of the elbow, while a tennis elbow affects the outside.
Will tennis elbow come back after treatment?
Recurrence is possible, especially if contributing habits or activities aren’t modified. Strengthening exercises, ergonomic adjustments, and avoiding overuse are key to long-term prevention.
Seek Medical Attention for Tennis Elbow
Don’t dismiss early tennis elbow symptoms. Untreated, this condition can severely hinder daily tasks, work, and sports. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is key to effective management and lasting recovery.
Quantum Orthopaedics offers a variety of services to ensure your fast and long-term recovery from tennis elbow and other orthopaedic conditions. Call us at 8028 4572 to book an appointment.

MMed (Orth), FRCS Orth & Tr (Edin)
Dr James Tan is a trusted orthopaedic surgeon in Singapore with over 10 years of experience in sports surgery and exercise medicine. He has treated athletes from Singapore’s national teams and professional football leagues. A specialist in knee, shoulder, and elbow injuries, Dr Tan is also skilled in minimally invasive tendon and ligament repair, cartilage and meniscus surgery, and joint replacement. He is a founding member of the Singapore Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Society and a fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons (Edinburgh). Committed to research and education, Dr Tan leads various research projects and serves as Adjunct Assistant Professor at both NUS and NTU medical schools.